Casablanca – Morocco’s automotive sector, a key pillar of the country’s industrial growth, is actively pursuing diversification strategies to safeguard its export revenues amid evolving global economic and geopolitical challenges. While the industry has thrived over the past two decades, fueled primarily by strong ties with European markets, recent developments have highlighted the risks of overreliance on a limited set of trade partners. In response, Morocco is expanding its commercial footprint across new regions and investing heavily in emerging technologies such as electric vehicles, positioning itself as a resilient and competitive player on the global automotive stage.
A rapidly growing industry anchored in Europe
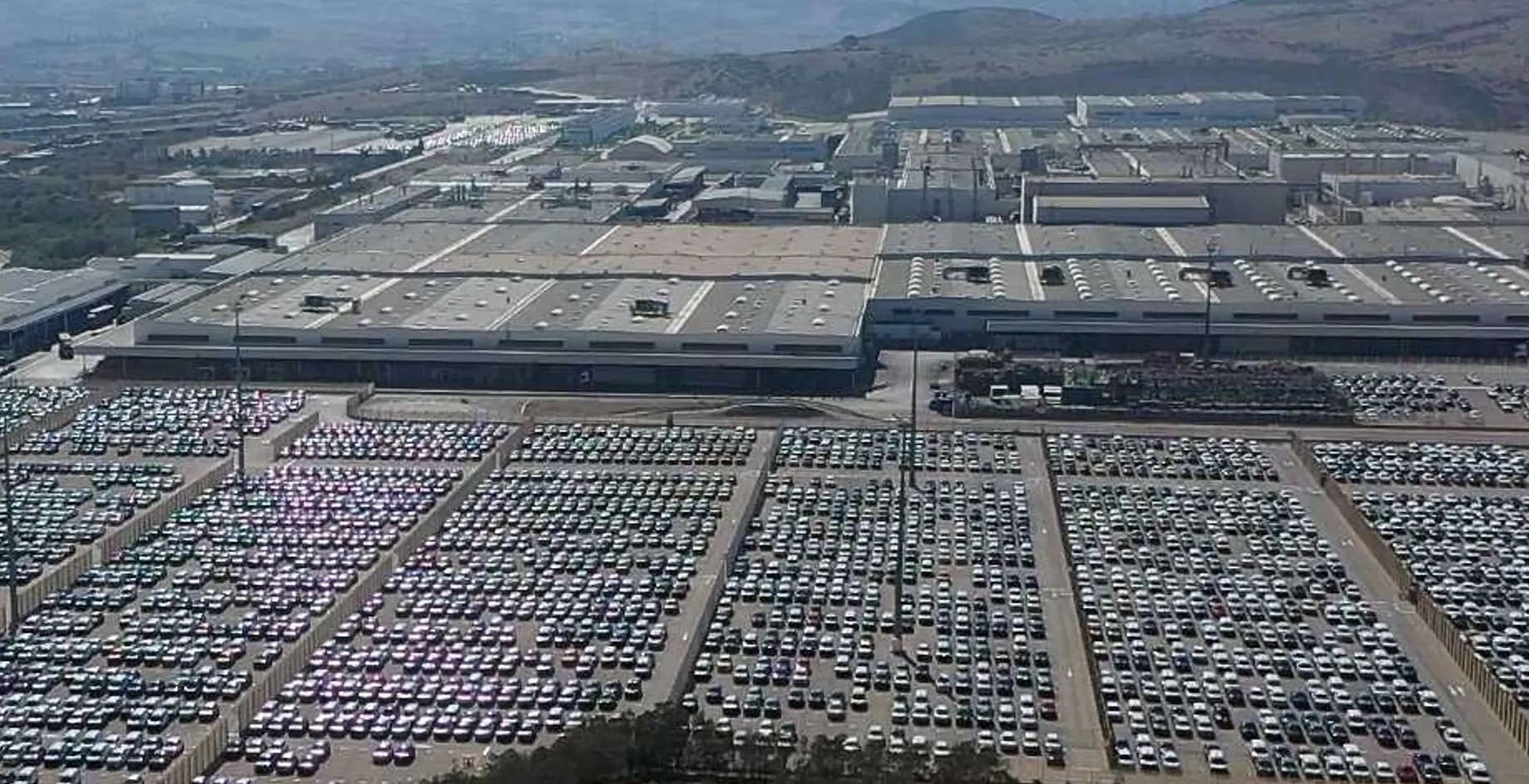
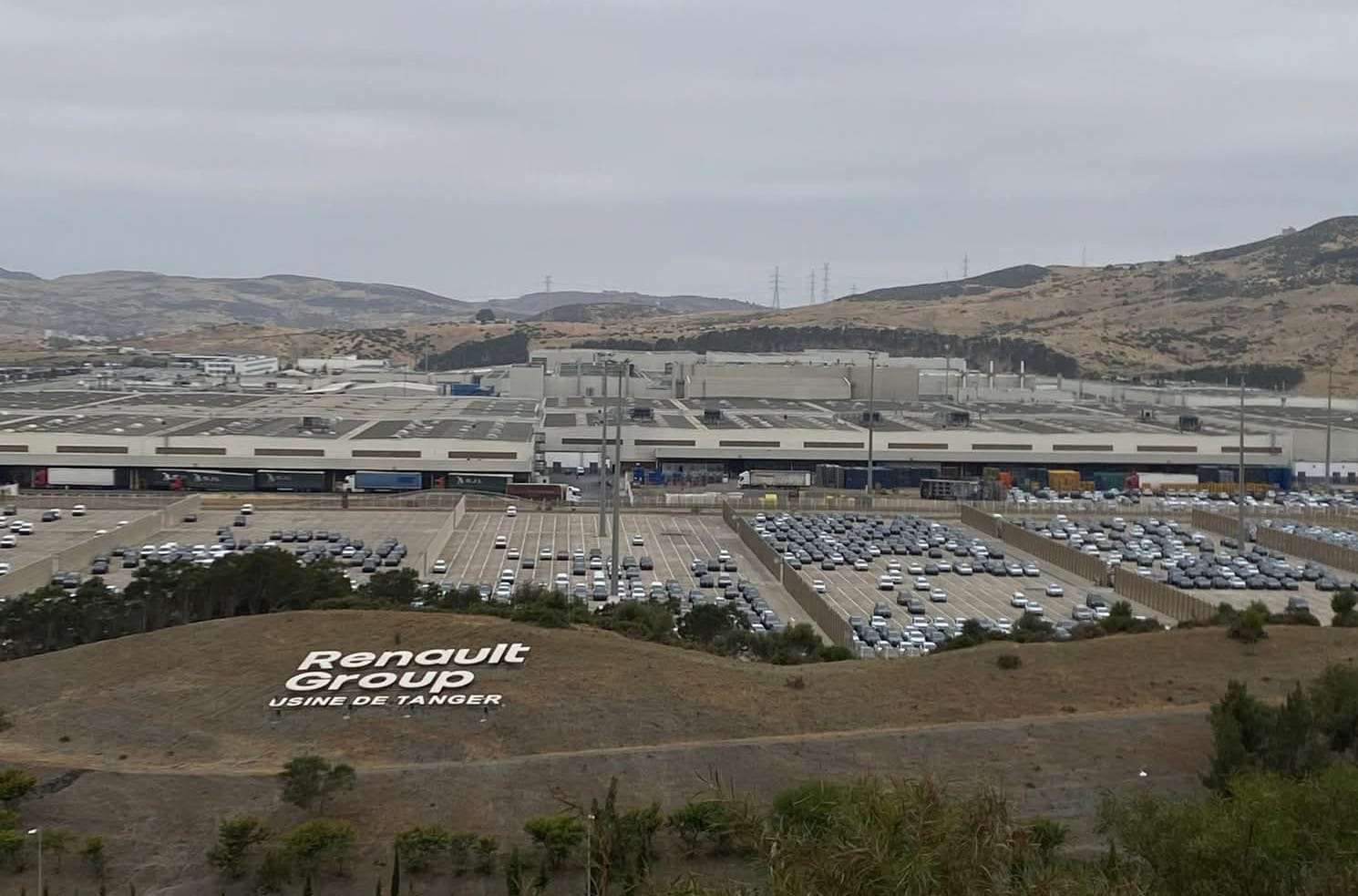
Since the early 2000s, Morocco’s automotive industry has experienced exponential growth, transforming the country into the leading automobile manufacturer in Africa. This growth has been driven by major global manufacturers like Renault and Stellantis, who have established significant production hubs in Morocco. In 2024, Renault assembled more than 413,000 vehicles at its two Moroccan plants, with most of these vehicles destined for European markets. Stellantis is also expanding its capacity at its Kenitra plant, aiming to double production to 400,000 units by 2030, including a rising share of electric vehicles.
Morocco’s automotive sector accounts for nearly 10% of the country’s exports and supports over 100,000 direct and indirect jobs. Approximately 90% of its production is exported to the European Union, making the continent Morocco’s principal market and a critical driver of the sector’s success. Favorable fiscal policies, efficient logistics infrastructure—particularly the Tanger Med port—and geographic proximity to Europe have been decisive factors in attracting investment and enabling efficient supply chains.
The risks of concentration and the need for diversification
Despite its impressive growth, the sector’s heavy dependence on Europe exposes it to considerable risks. Economic fluctuations, trade tensions, and regulatory changes in the EU could have immediate and significant impacts on Morocco’s automotive exports. The COVID-19 pandemic and the recent increase in global trade protectionism have underscored the vulnerability of concentrated supply chains.
Unlike some competitors, Morocco has been relatively spared from U.S. tariffs due to its limited market presence in North America. However, the country remains exposed to the economic health of Europe, which accounts for the lion’s share of its export activity. Recognizing this risk, Moroccan policymakers and industry leaders have prioritized expanding export destinations beyond the EU to reduce vulnerability and sustain long-term growth.
Expanding to new markets
To mitigate concentration risk, Morocco is actively broadening its commercial reach toward emerging markets in Africa, the Middle East, and the United Kingdom. The country is leveraging the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) to access a wider African market, while also strengthening bilateral trade ties with Gulf countries and the UK. These efforts are supported by regular trade missions and promotional campaigns designed to establish new partnerships and increase Moroccan automotive products’ visibility in these regions.
This geographical diversification not only opens new revenue streams but also reduces the impact of potential economic slowdowns or regulatory changes in Europe. Moreover, diversifying partner countries enhances Morocco’s resilience against geopolitical tensions affecting global trade.
Investing in electric and sustainable mobility
Alongside geographic diversification, Morocco is prioritizing technological innovation, particularly in electric vehicle (EV) production. The country is capitalizing on its natural resource advantages—most notably phosphate, a key material in lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries—to attract investment in EV manufacturing and related industries.
In 2024, Morocco registered 12 new industrial projects related to electric vehicles, surpassing comparable figures in South Africa and signaling its ambitions to become a regional leader in this field. This shift toward sustainable mobility aligns with global trends and growing demand for cleaner transportation solutions.
Moroccan authorities are supporting this transition through targeted policies, including incentives for investors, efforts to develop local supply chains, and substantial investment in workforce training. The Tanger Med port, with the capacity to handle up to one million vehicles annually, and industrial zones like Tanger Automotive City, provide a strong logistical and operational foundation for EV production and export.
Infrastructure and human capital development
To underpin its diversification and innovation strategies, Morocco is investing heavily in infrastructure upgrades. Modernizing ports, road networks, and industrial zones is essential to streamline production and export operations, reduce costs, and enhance competitiveness.
In addition, the country is focusing on workforce development, recognizing the importance of skilled labor in maintaining high-quality production and driving innovation. Training programs and partnerships with European research centers are being expanded to improve technical skills and foster technological know-how in the automotive sector.
Challenges ahead
Despite strong momentum, Morocco’s automotive sector faces significant challenges. Competition is increasing not only from other African countries seeking to grow their own automotive industries but also from emerging global players investing in EV manufacturing. Environmental regulations and the need to maintain a favorable investment climate also require continuous attention.
Furthermore, ensuring that local supply chains can meet the demands of advanced vehicle production remains a priority. The sector’s long-term success will depend on its ability to innovate, adapt, and effectively manage risks associated with global market fluctuations.
Morocco’s automotive industry stands at a critical juncture, balancing impressive growth with the need to mitigate risks linked to market concentration. Through deliberate diversification of export markets and strategic investments in electric vehicles and infrastructure, Morocco aims to build a more resilient and future-ready automotive sector. If these efforts continue, the country is well-positioned to maintain its leadership role in Africa and expand its footprint in the evolving global automotive landscape.